User Guide
YellowBook is a desktop application for university students who are involved in many projects to organize their project contacts and tasks. As a user of YellowBook, you will be able to:
- add contacts
- update contact details
- add tasks
- update task details
- track your task completion progress
- get task reminders
- sort tasks by deadlines
- and more!
As YellowBook is optimised for use via a Command Line Interface (CLI), in which all functionality is achieved through typing commands, you will benefit greatly from the use of this application if you are a fast typer.
Read on to find out more about YellowBook’s features!
Table of Contents
- Table of Contents
- Purpose
- Quick start
- Sample Usage
- Icons
- Features
- Section 1: Contacts
-
Section 2: Tasks
- Adding a task:
addT - Listing all non-archived tasks:
listT - Listing all archived tasks:
listAT - Deleting a task:
deleteT - Editing a task:
editT - Finding a task:
findT - Filtering tasks by label:
filterT - Marking a task as complete:
markT - Marking a task as incomplete:
unmarkT - Archiving a task:
archiveT - Unarchiving a task:
unarchiveT - Listing tasks with deadlines up to and including the specified date:
remindT - Showing the percentage of tasks with the specified tags that are completed:
progressT - Sorting all tasks by deadline:
sortD - Sorting all tasks by id:
sortI
- Adding a task:
- Section 3: Labels
- Section 4: Other Useful Features
- Automatic tab switching
- YellowBook data
- FAQ
- Command summary
Purpose
Welcome to YellowBook’s user guide.
If you are a first-time user, this user guide will walk you through setting up YellowBook. The sample usage section will also provide a brief tutorial for you to get familiar with the commands and command formats.
This user guide also provides comprehensive explanations so that you know how to use all the features in YellowBook.
Quick start
-
Ensure you have Java
11or above installed in your Computer. (Installation Guide) -
Download the latest
yellowbook.jarfrom here. -
Copy the file to the folder you want to use as the home folder for your YellowBook.
-
Double-click the file to start the app. The GUI, as shown in the image below, should appear in a few seconds. Note how the app contains some sample data.
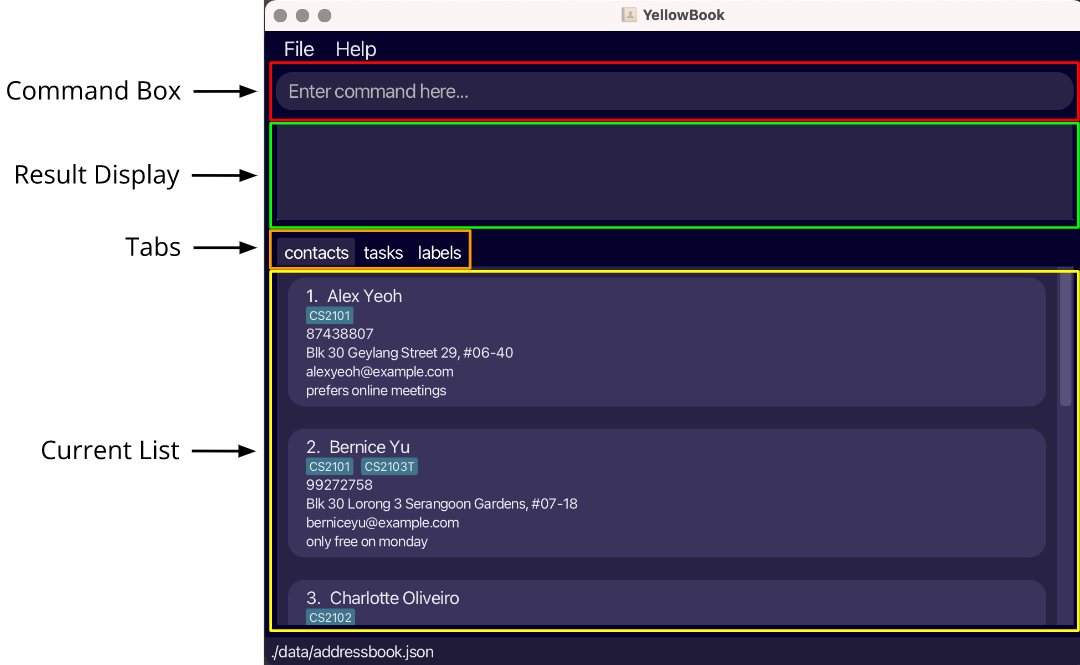
Fig.1 - App UI -
Try out some commands from the Sample Usage section.
-
Refer to the Features below for details of each command.
Sample Usage
To better understand the usage of YellowBook, we have provided a usage scenario of YellowBook below. We encourage all first-time users to follow along to gain a general understanding of the commands available.
-
YellowBook comes with a list of sample contacts and tasks by default.
-
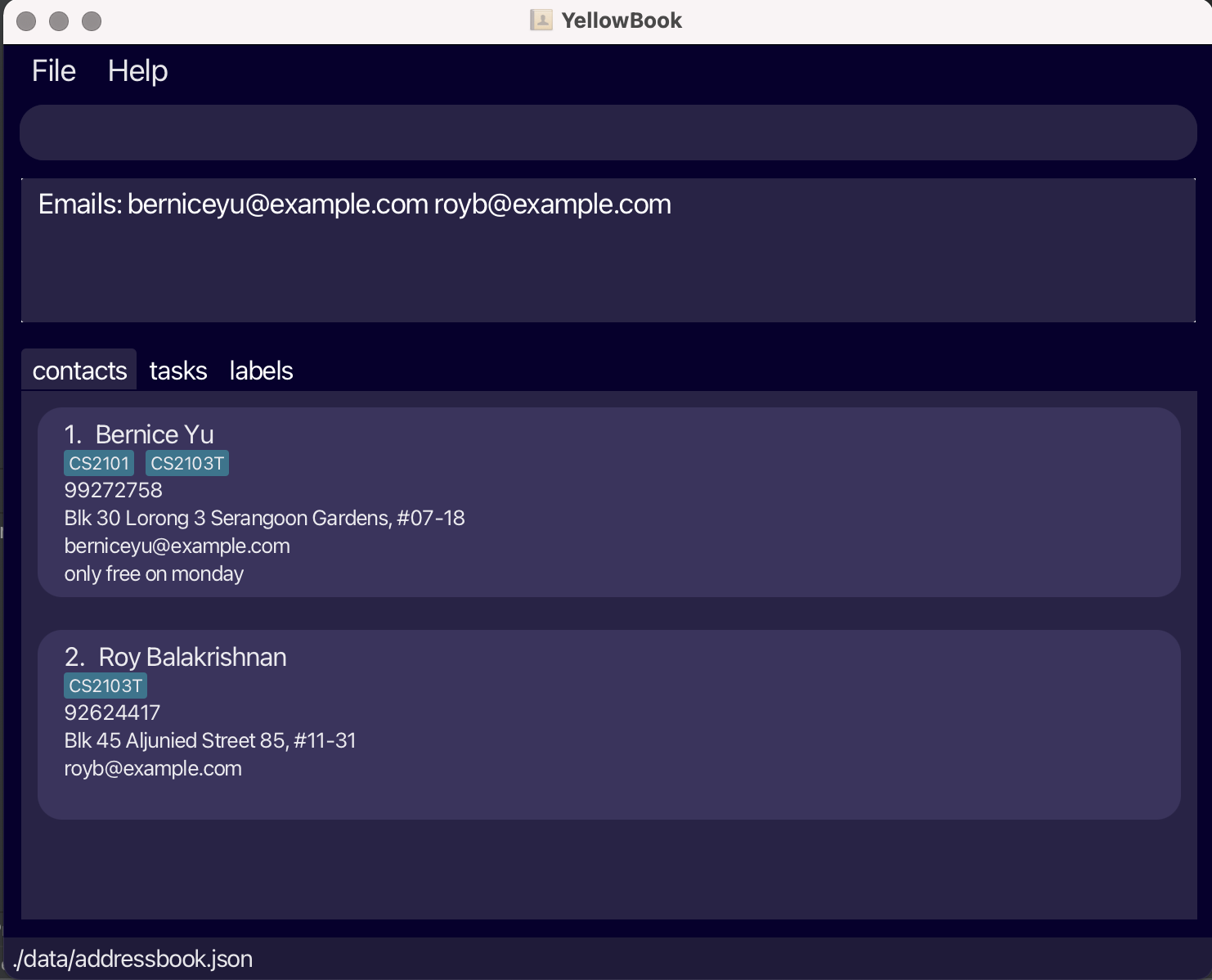
Let’s start by listing all the contacts in YellowBook. Type
listCin the command box and press Enter to execute it. You should see a list of contacts. Try usinglistTto list all the tasks.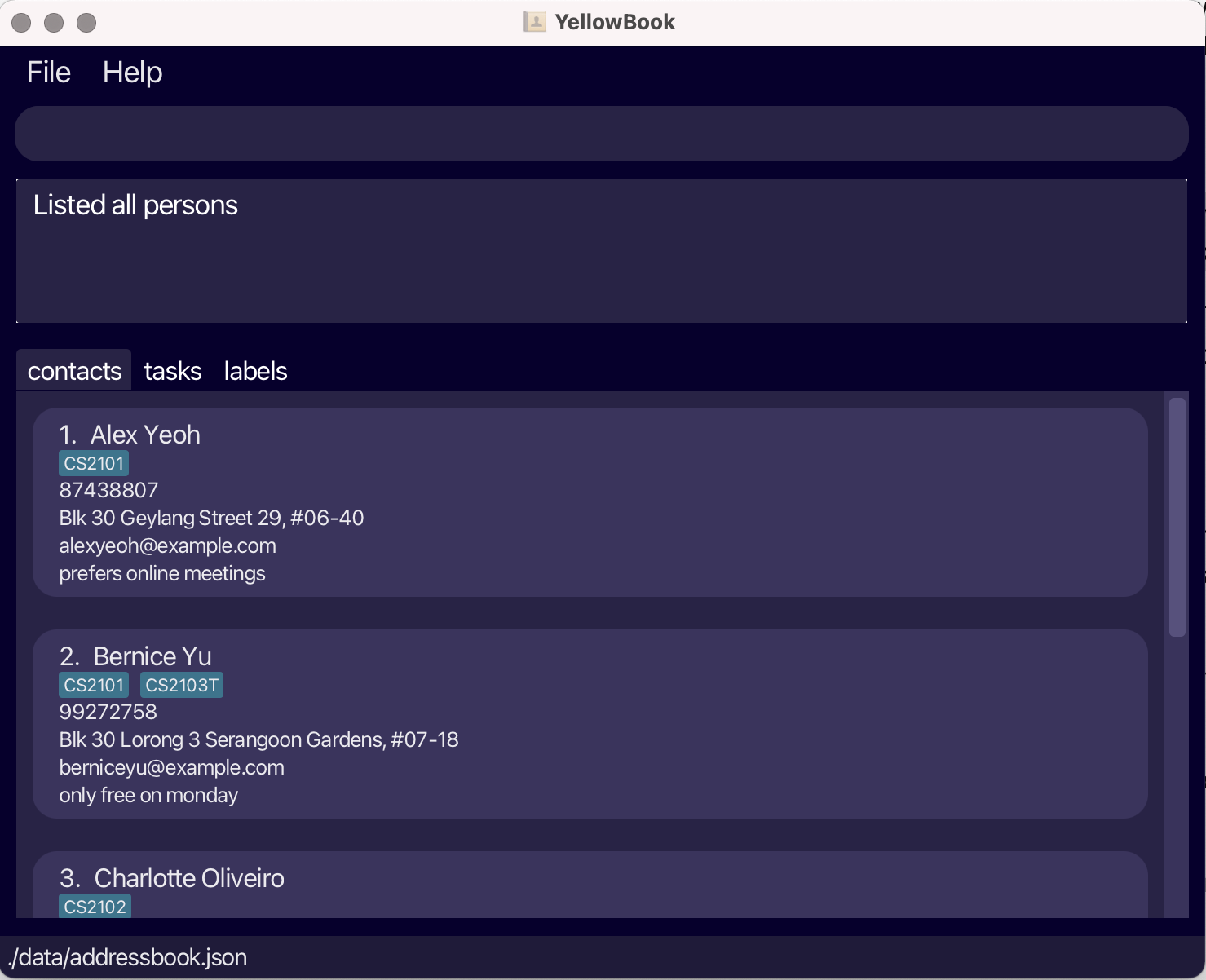
Fig.2 - Result of listC 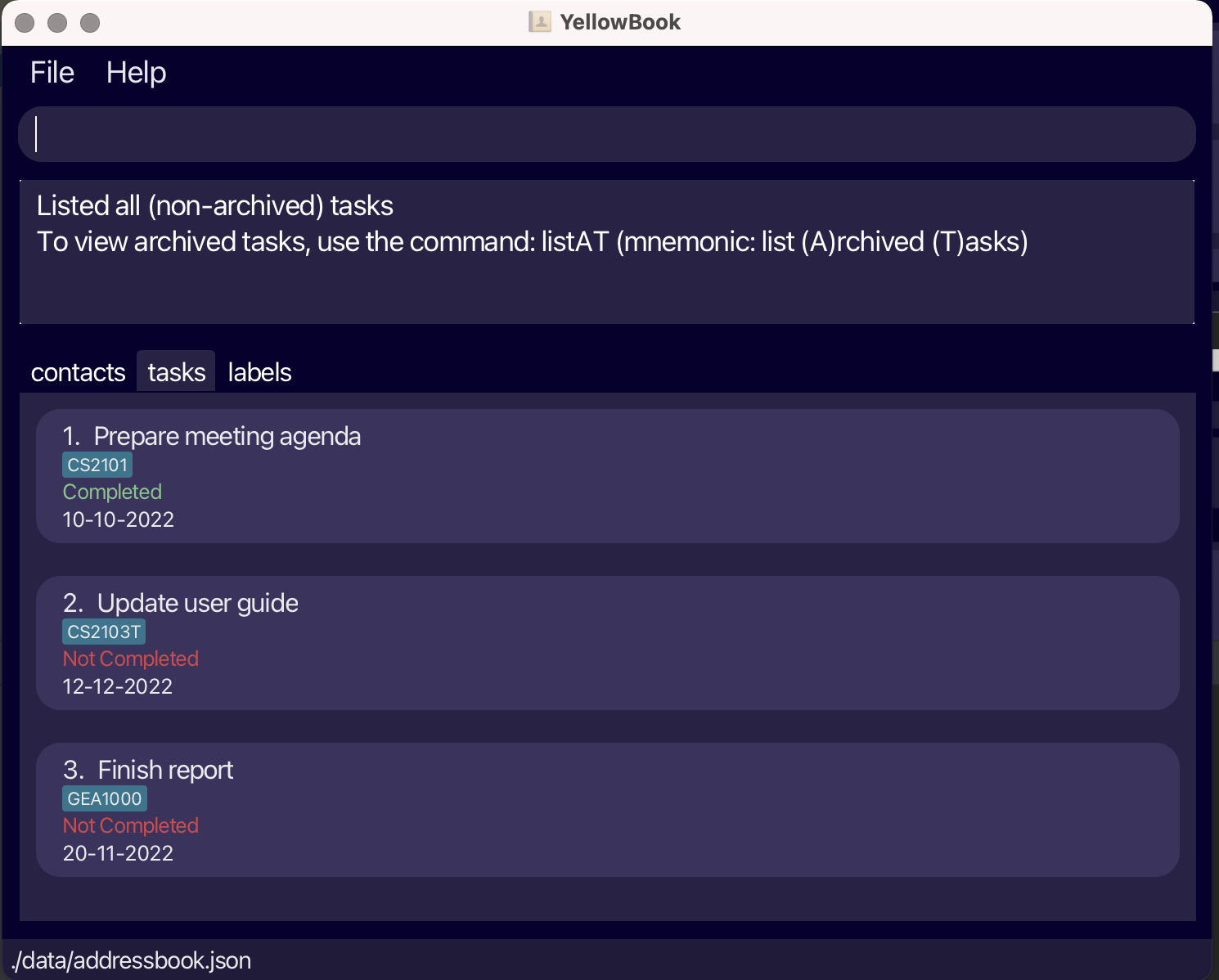
Fig.3 - Result of listT -
Now that you can navigate between the contact and task lists, let’s add a new contact. Type
addC n/Elmo p/91238888 e/elmo@sesamestreet.com a/sesame streetin the command box and press Enter to execute it. You should see a message indicating that the contact has been added successfully and Elmo will appear in your contact list.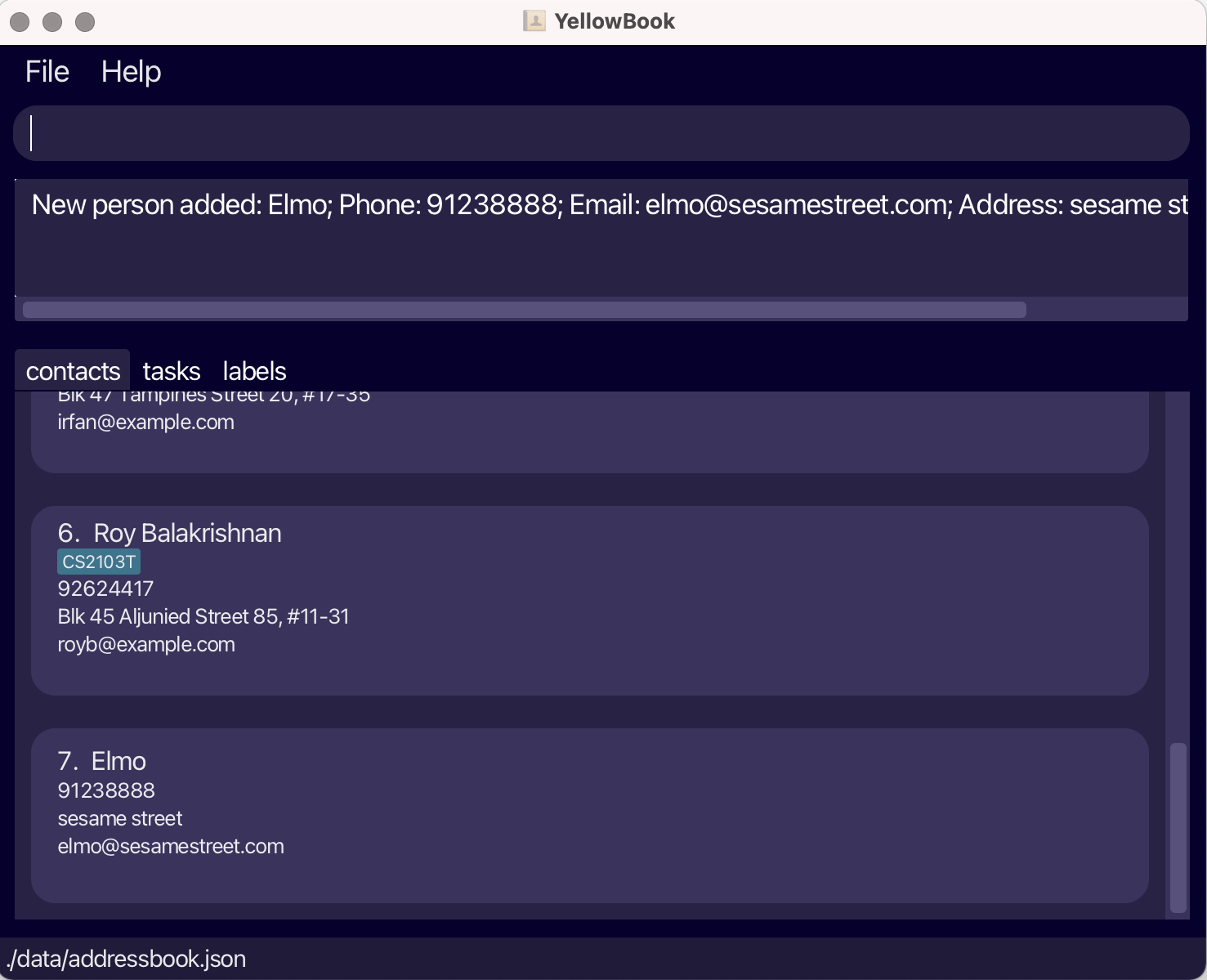
Fig.4 - Result of addC -
YellowBook also allows you to add tasks, to add homework task with deadline of 25 December 2022. Type
addT d/complete homework D/25-12-2022in the command box and press Enter to execute it. You should see a message indicating that the task has been added successfully and the task will appear in your task list.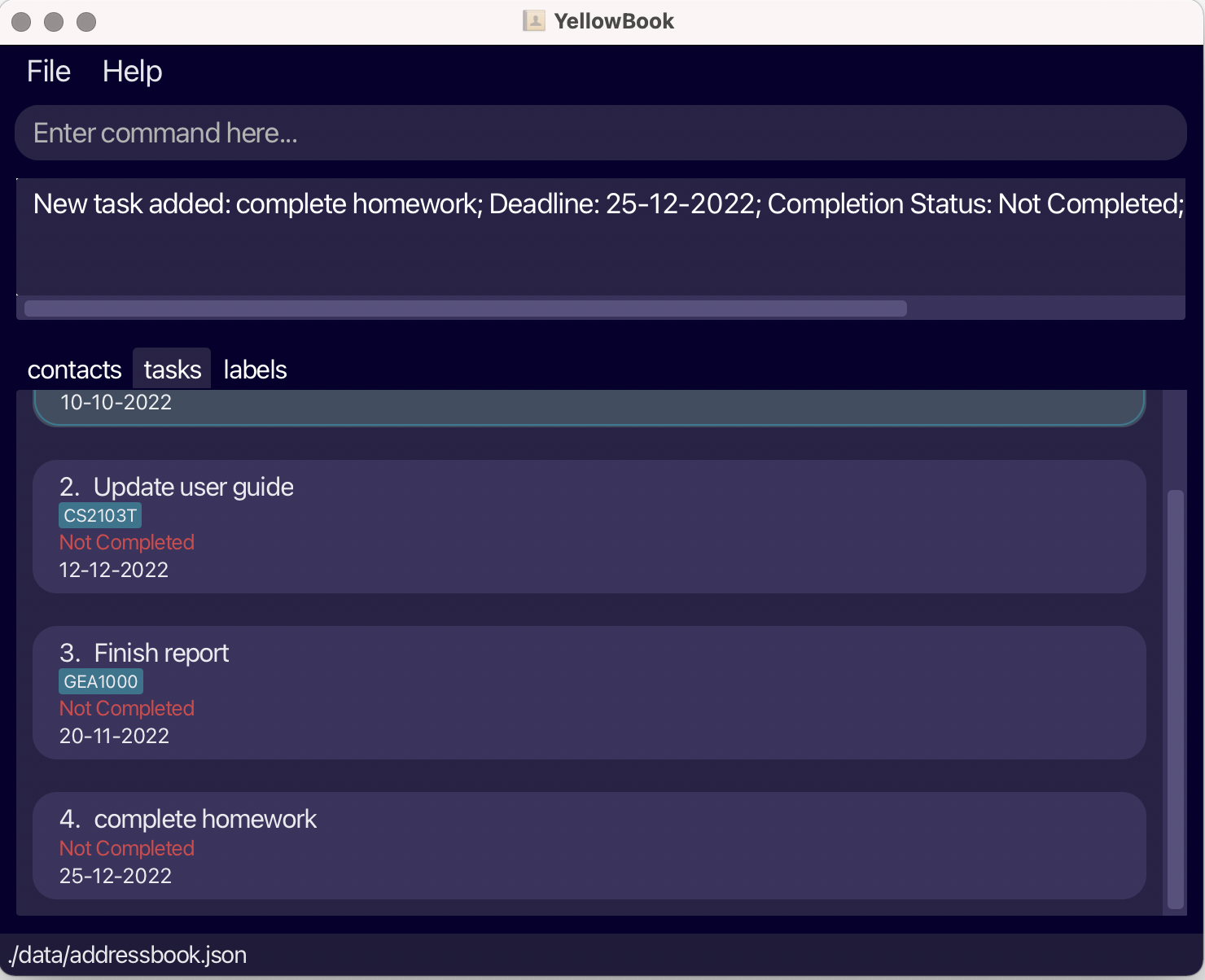
Fig.5 - Result of addT -
Now that you know the basic commands, try following the guide for the label command to tag the newly added
Elmocontact asfriend. -
When you feel ready to use YellowBook for your own contacts and tasks, type
clearto remove all the sample data from YellowBook.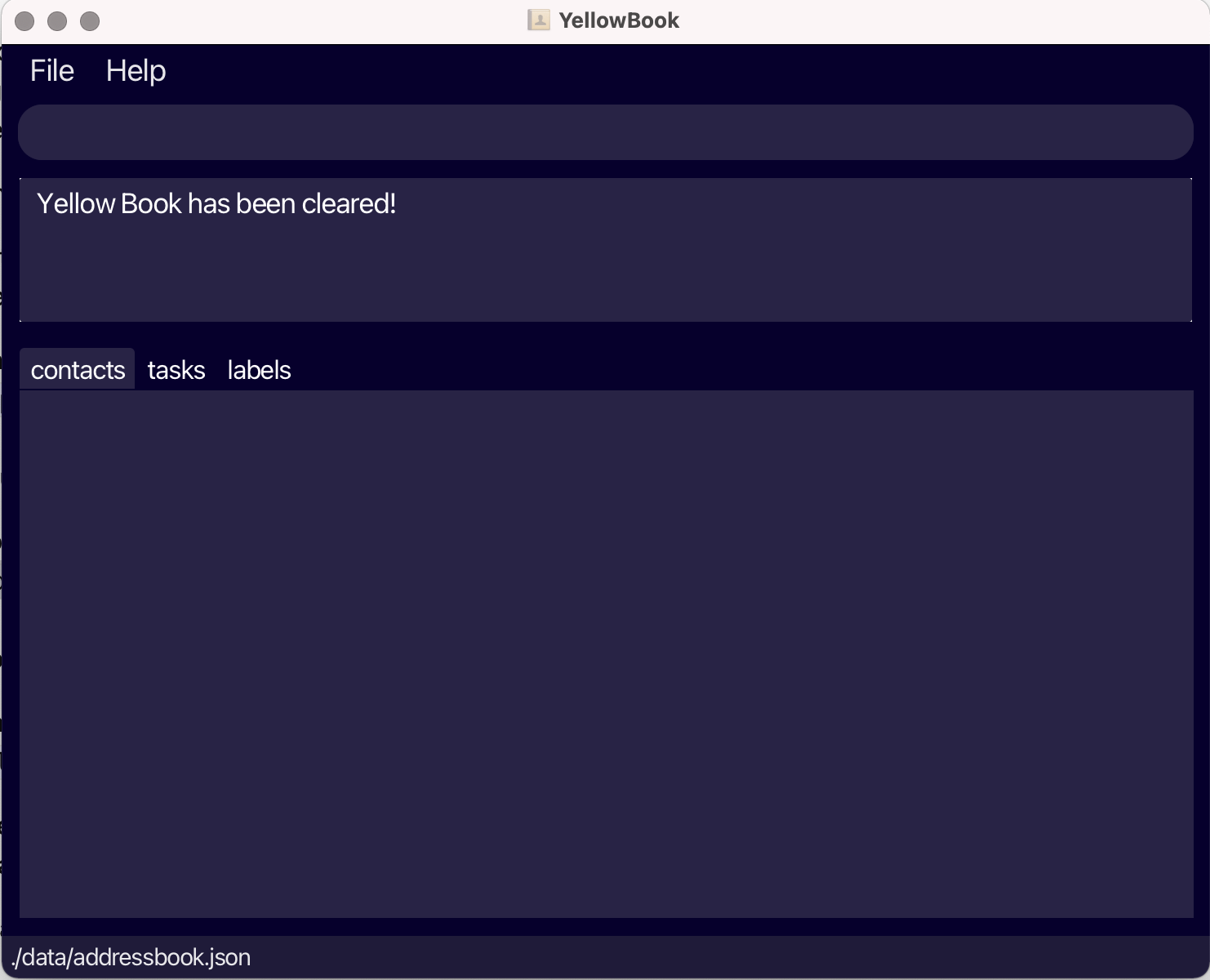
Fig.6 - Result of clear command -
YellowBook’s commands are mnemonically named. A Command Summary with these helpful tips can be found below.
Icons
Meaning of the icons used:
![]() : Useful information
: Useful information
![]() : Tip
: Tip
![]() : Warning on incorrect usage
: Warning on incorrect usage
![]() : Caution
: Caution
Features
![]() Command format:
Command format:
-
Words in
UPPER_CASEare the parameters to be supplied by the user.
e.g. inadd n/NAME,NAMEis a parameter which can be used asadd n/John. -
Items in square brackets are optional.
e.gn/NAME [r/REMARK]can be used asn/John Doe r/friendor asn/John Doe. -
Items with
… after them can be used multiple times including zero times.
e.g.[t/LABEL]…can be used ast/friend,t/friend t/familyetc. -
Parameters can be in any order.
e.g. if the command specifiesn/NAME p/PHONE_NUMBER,p/PHONE_NUMBER n/NAMEis also acceptable. -
If a parameter is expected only once in the command but you specified it multiple times, only the last occurrence of the parameter will be taken.
e.g. if you specifyp/12341234 p/56785678, onlyp/56785678will be taken. -
Extraneous parameters for commands that do not take in parameters (such as
listC,listT) will be ignored.
e.g. if the command specifieshelp 123, it will be interpreted ashelp.
Section 1: Contacts
These commands allow you to maintain a list of business contacts that you meet for collaborative projects. Whether it be for a school project or an internship, store all their details in one place for easy look-up. Contact management has never been this simple.
![]() Notes on contacts
Notes on contacts
-
Contacts have no labels by default.
-
Contact names are limited to alphanumeric characters and spaces. There must be at least one alphanumeric character.
-
Contact phone numbers are limited to numeric characters and must be at least three digits long.
-
Contact emails should be of the format local-part@domain.
The local-part is limited to alphanumeric characters and four special characters “+”, “_”, “.”, and “-“. However, the local-part may not start or end with any special characters.
The domain name consists of domain labels separated by periods, and should end with a domain label at least two characters long. Each domain label should consist of alphanumeric characters, separated only by hyphens, if any. Domain labels must start and end with alphanumeric characters. -
Contact addresses can take any values, but must consist of at least one non-space character.
-
Contact remarks are limited to alphanumeric characters and spaces.
Adding a contact: addC
Adds a contact to the contact list.
Format: addC n/NAME p/PHONE_NUMBER e/EMAIL a/ADDRESS [r/REMARK]
![]() There will be an error if you:
There will be an error if you:
-
Do not adhere to field constraints.
-
Add a contact that is the same as one already in the address book. Two contacts are the same if they have the same email or phone number.
Example:
-
addC n/John Doe p/98765432 e/johnd@example.com a/John street, block 123, #01-01 -
addC n/Betsy Crowe e/betsycrowe@example.com a/Newgate Prison p/1234567 r/Weird person
Listing all contacts: listC
Shows all contacts stored in the contact list.
Format: listC
Deleting a contact: deleteC
Deletes a contact from the contact list.
Format: deleteC INDEX
- Index of a contact is its index number on the currently shown contact list.
![]() There will be an error if you:
There will be an error if you:
-
Enter 0 or a negative number as INDEX.
-
Enter a number greater than the currently shown list size as INDEX.
Examples:
-
listCfollowed bydeleteC 1deletes the first contact in the address book. -
findC n/Johnfollowed bydeleteC 1deletes the first result of thefindCcommand.
Editing a contact: editC
Edits the information fields (e.g. name, mobile number, email address) of an existing contact in the contact list.
Format: editC INDEX [n/NAME] [p/PHONE] [e/EMAIL] [a/ADDRESS] [r/REMARK]
-
Index of a contact is its index number on the currently shown contact list.
-
Input values will replace existing values.
![]() There will be an error if you:
There will be an error if you:
-
Do not adhere to field constraints.
-
Edit the contact such that it becomes a duplicate contact to one already in the contact list. Two contacts are the same if they have the same email or phone number.
-
Enter 0 or a negative number as INDEX.
-
Enter a number greater than the currently shown list size as INDEX.
-
Do not provide at least one of the optional fields.
Example:
-
editC 1 n/John p/12345678edits the first contact’s name to be John and phone number to be 12345678.
Finding a contact: findC
Finds a contact using one or more information fields (e.g. name, phone number, email, address, and/or remark).
Format: findC [n/NAME] [p/PHONE] [e/EMAIL] [a/ADDRESS] [r/REMARK]
-
The search is case-insensitive, e.g.
dr doofenshmirtzwill matchDr Doofenshmirtz. -
Only full words will be matched, e.g.
Johnwill not matchJohnny. -
Contacts matching at least one keyword will be returned, e.g.
n/Perry Drwill match contacts with namePerry the PlatypusandDr Doofenshmirtz. -
Successive
findCcommands are not cumulative, e.g.findC n/Johnfollowed byfindC n/Doewill return the same result asfindC n/Doe.
![]() There will be an error if you:
There will be an error if you:
-
Do not adhere to the field constraints.
-
Do not provide at least one optional field.
Examples:
-
findC n/flynnwill returnCandace FlynnandPhineas Flynn. -
findC n/john p/12345678 e/john@gmail.com a/123will return contacts with name containing the wordjohn, phone number12345678, emailjohn@gmail.com, and address containing123.
Filtering contacts by label: filterC
Filters contacts whose label(s) contain any of the given keywords.
Format: filterC KEYWORD [MORE_KEYWORDS]...
-
The filter is case-sensitive, e.g.
cs2103twill not matchCS2103T. -
Only full words will be matched, e.g.
mathwill not matchmathematics. -
Successive
filterCcommands are not cumulative, e.g.filterC cs2101followed byfilterC cs2103twill return the same result asfilterC cs2103t.
![]() There will be an error if you:
There will be an error if you:
- Do not adhere to label name constraints. Label names must be alphanumeric with no spaces.
Examples:
-
filterC cs2103twill return contacts with labelcs2103t. -
filterC cs2103t cs2101will return contacts with labelscs2103torcs2101.
Copying contact emails by label: copyC
Displays a string of emails of contacts with a label that matches the given keyword for easier copy-pasting.
Format: copyC KEYWORD
-
copyCis case-sensitive, e.g.CS2103Twill not matchcs2103t. -
Only full words will be matched, e.g.
cs2103twill not matchcs2103.
![]() There will be an error if you:
There will be an error if you:
- Do not adhere to label name constraints. Label names must be alphanumeric with no spaces.
Example:
-
copyC CS2103Treturns a string of emails of contacts that contain the labelCS2103T.
Section 2: Tasks
These commands allow you to maintain a handy to-do list so you can prioritise what needs to be done first. Tasks can be archived once they are completed, so you can keep track of your progress. Monitor your progress, track deadlines and archive tasks with a few simple commands. Leave your task management to YellowBook, so you can do your best work.
![]() Notes on tasks:
Notes on tasks:
-
Tasks have no labels by default.
-
Task description should only contain alphanumeric characters and spaces, and it should not be blank.
-
Task deadline must be in the format dd-mm-yyyy, e.g.
25-12-2022.
Adding a task: addT
Adds a task to the task list.
Format: addT d/DESCRIPTION D/DEADLINE
-
Newly added tasks are marked as not done by default.
-
Tasks that are past their deadline can still be added since overdue tasks might have to be completed still.
![]() There will be an error if you:
There will be an error if you:
-
Add a task that is the same as one already in the address book. Two tasks are the same if they have the same description, deadline and labels.
-
Do not adhere to field constraints.
Example:
-
addT d/buy milk D/12-09-2022will add the task “buy milk” with deadline 12 September 2022.
Listing all non-archived tasks: listT
Shows all (non-archived) tasks stored in the task list.
Format: listT
- Newly added tasks are marked as unarchived by default.
![]()
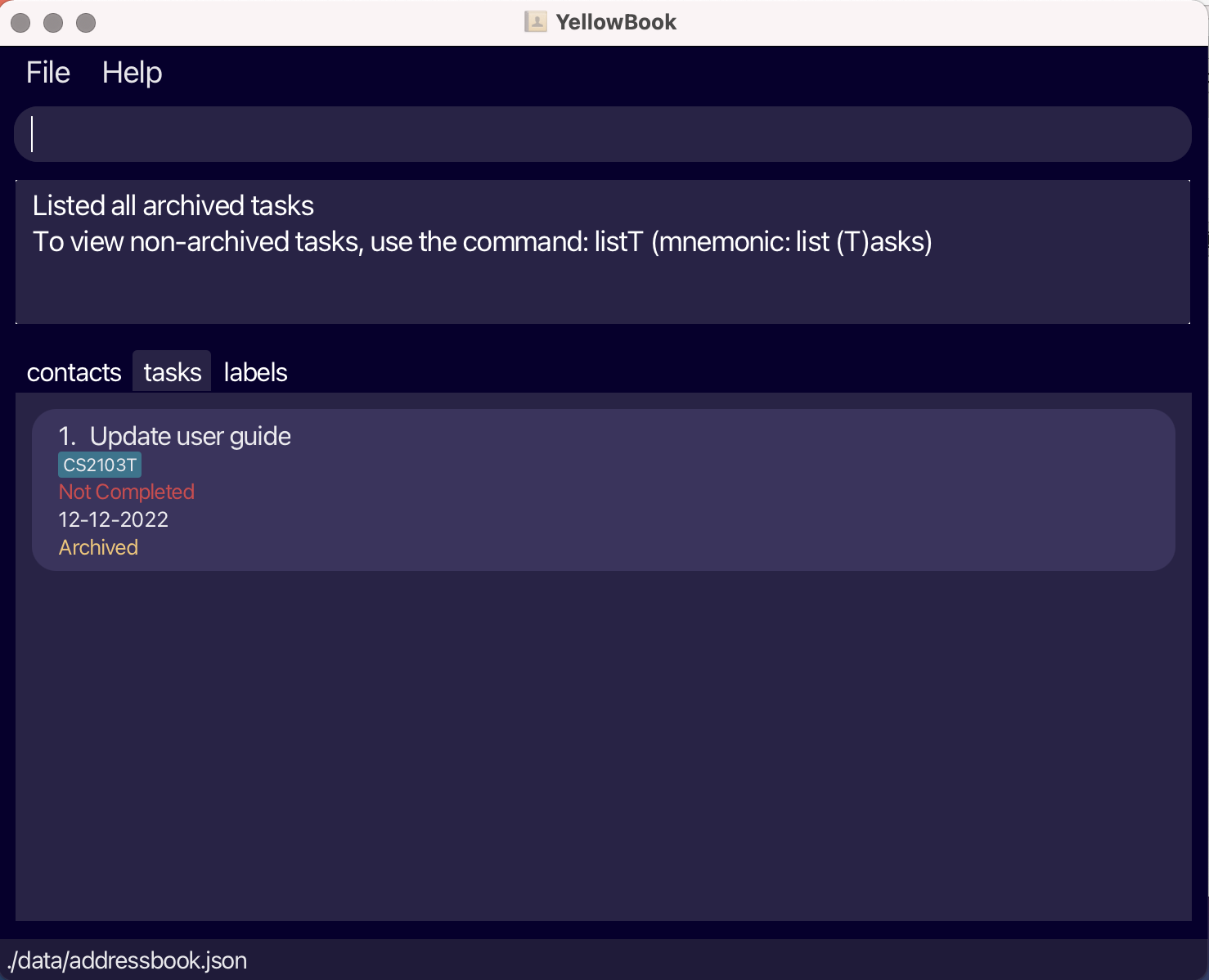
Listing all archived tasks: listAT
Shows all archived tasks stored in the task list.
Format: listAT
![]()
-
Unarchived tasks can be viewed using the
listTcommand. -
Task can be unarchived using the
unarchiveTcommand.
Deleting a task: deleteT
Deletes a task from the task list.
Format: deleteT INDEX
-
Index of a task is its index number on the currently shown task list.
-
INDEX must be a positive integer more than 0.
![]() There will be an error if you:
There will be an error if you:
-
Enter 0 or a negative number as INDEX.
-
Enter a number greater than the currently shown list size as INDEX.
Examples:
-
listTfollowed bydeleteT 1deletes the first task in the task list. -
findT d/bookfollowed bydeleteT 1deletes the first result of thefindTcommand.
Editing a task: editT
Edits the information fields (e.g. description, deadline) of an existing task in the task list.
Format: editT INDEX [d/DESCRIPTION] [D/DEADLINE]
-
Index of a task is its index number on the currently shown task list.
-
Input values will replace existing values.
![]() There will be an error if you:
There will be an error if you:
-
Do not adhere to field constraints.
-
Enter 0 or a negative number as INDEX.
-
Enter a number greater than the currently shown list size as INDEX.
-
Do not provide at least one of the optional fields.
-
Edit the task such that it becomes a duplicate task to one already in the task list. Two tasks are the same if they have the same description, deadline and labels.
Example:
-
editT 1 d/sleep D/22-10-2022edits the first task’s description to be “sleep” and deadline to be 22-10-2022.
Finding a task: findT
Finds tasks using one or more information fields (e.g. description, deadline, and/or completion status).
Format: findT [d/DESCRIPTION] [D/DEADLINE] [s/STATUS]
-
Task status must be either
completeorincomplete. -
Both archived and unarchived tasks containing the search terms will be displayed.
-
The search is case-insensitive, e.g.
homeworkwill matchHOMEWORK. -
Only full words will be matched, e.g.
mathwill not matchmathematics. -
Task descriptions matching at least one keyword will be returned, e.g.
d/cs2103t cs2101will matchcs2103t tutorialandcs2101 reflection. -
Successive
findTcommands are not cumulative, e.g.findT d/mathfollowed byfindT d/homeworkwill return the same result asfindT n/homework.
![]() There will be an error if you:
There will be an error if you:
-
Do not adhere to the field constraints.
-
Do not provide at least one optional field.
Examples:
-
findT s/incompletewill return tasks that are not complete. -
findT d/cs2103t D/25-12-2022 s/completewill return tasks with descriptions containingcs2103t, deadline25th December 2022, and completion statuscomplete.
Filtering tasks by label: filterT
Filters tasks whose label(s) contain any of the given keywords.
Format: filterT KEYWORD [MORE_KEYWORDS]...
-
Both archived and unarchived tasks containing specified labels will be displayed.
-
The filter is case-sensitive, e.g.
cs2103twill not matchCS2103T. -
Only full words will be matched, e.g.
mathwill not matchmathematics. -
Successive
filterTcommands are not cumulative, e.g.filterT cs2103tfollowed byfilterT mathwill return the same result asfilterT math.
![]() There will be an error if you:
There will be an error if you:
- Do not adhere to label name constraints. Label names must be alphanumeric with no spaces.
Examples:
-
filterT cs2103twill return tasks with labelcs2103t. -
filterT cs2103t cs2101will return tasks with labelscs2103torcs2101.
Marking a task as complete: markT
Marks a task in the task list as complete.
Format: markT INDEX
- Index of a task is its index number on the currently shown task list.
![]() There will be an error if you:
There will be an error if you:
-
Enter 0 or a negative number as INDEX.
-
Enter a number greater than the currently shown list size as INDEX.
Examples:
-
listTfollowed bymarkT 1marks the first task in the displayed task list as done. -
findT d/bookfollowed bymarkT 1marks the first result of thefindTcommand as done.
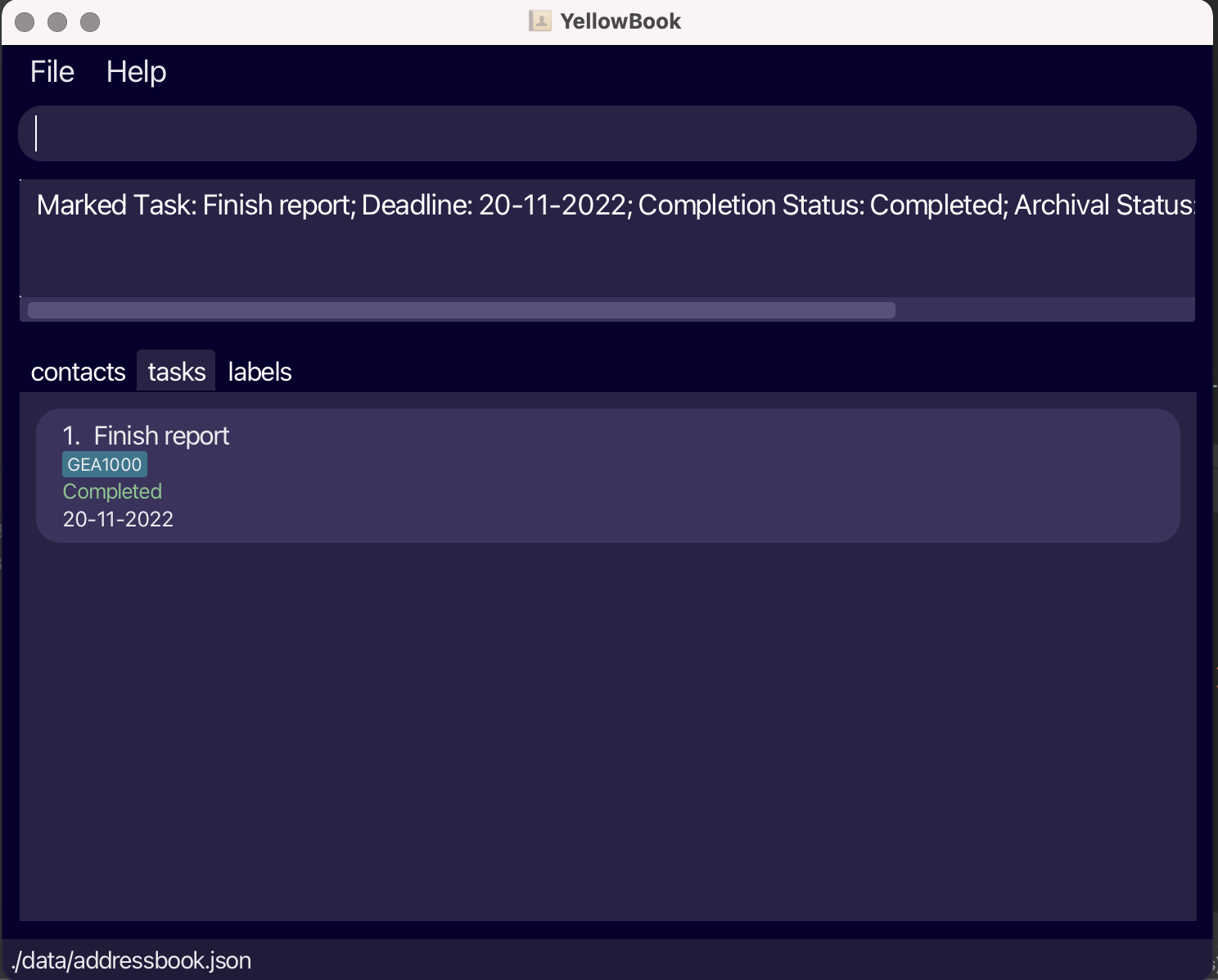
Marking a task as incomplete: unmarkT
Marks a task in the task list as incomplete.
Format: unmarkT INDEX
- Index of a task is its index number on the currently shown task list.
![]() There will be an error if you:
There will be an error if you:
-
Enter 0 or a negative number as INDEX.
-
Enter a number greater than the currently shown list size as INDEX.
Examples:
-
listTfollowed byunmarkT 1marks the first task in the displayed task list as undone. -
findT d/bookfollowed byunmarkT 1marks the first result of thefindTcommand as undone.
Archiving a task: archiveT
Archives a task in the displayed task list, removing it from main (unarchived) task list.
Format: archiveT INDEX
- Archived task list will be displayed after executing this command.
![]() There will be an error if you:
There will be an error if you:
-
Enter 0 or a negative number as INDEX.
-
Enter a number greater than the size of displayed task list as INDEX.
Examples:
-
listTfollowed byarchiveT 1archives the first task in the displayed task list. -
findT d/bookfollowed byarchiveT 1archives the first result of thefindTcommand.
Unarchiving a task: unarchiveT
Unarchives a task in the displayed task list, adding it to the main (unarchived) task list.
Format: unarchiveT INDEX
- Main (unarchived) task list will be displayed after executing this command.
![]() There will be an error if you:
There will be an error if you:
-
Enter 0 or a negative number as INDEX.
-
Enter a number greater than the size of displayed task list as INDEX.
Examples:
-
listATfollowed byunarchiveT 1unarchives the first task in the displayed task list. -
findT d/bookfollowed byunarchiveT 1unarchives the first result of thefindTcommand.
Listing tasks with deadlines up to and including the specified date: remindT
Lists tasks in task list with deadlines up to and including the specified date.
Format: remindT DEADLINE
-
Both completed and incomplete tasks are listed.
-
Task with deadlines that are already past are also listed.
![]() There will be an error if you:
There will be an error if you:
- Do not adhere to deadline constraints. Deadline must be in dd-mm-yyyy format.
Example:
-
remindT 12-09-2022will list all tasks with deadlines up to and including 12-09-2022.
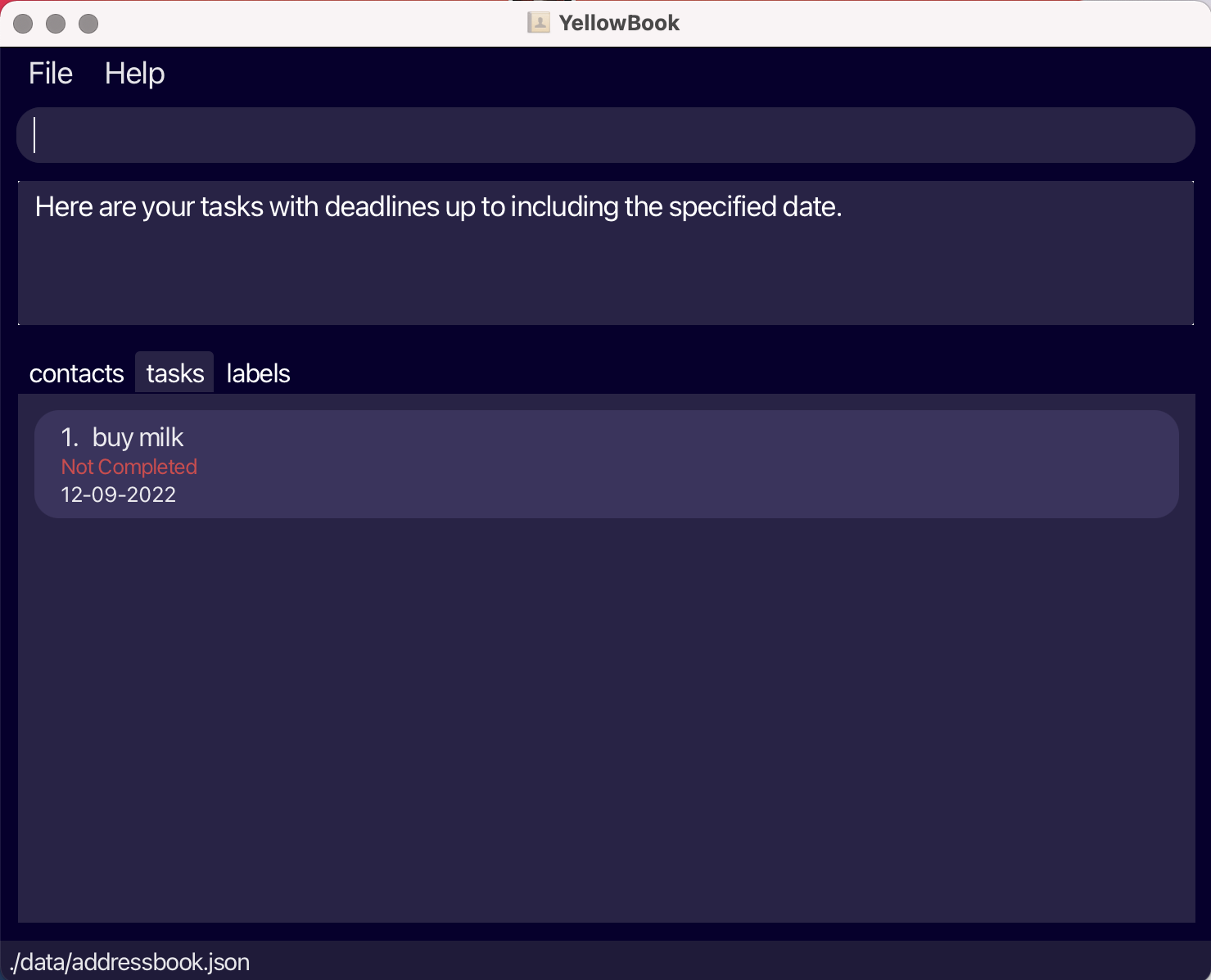
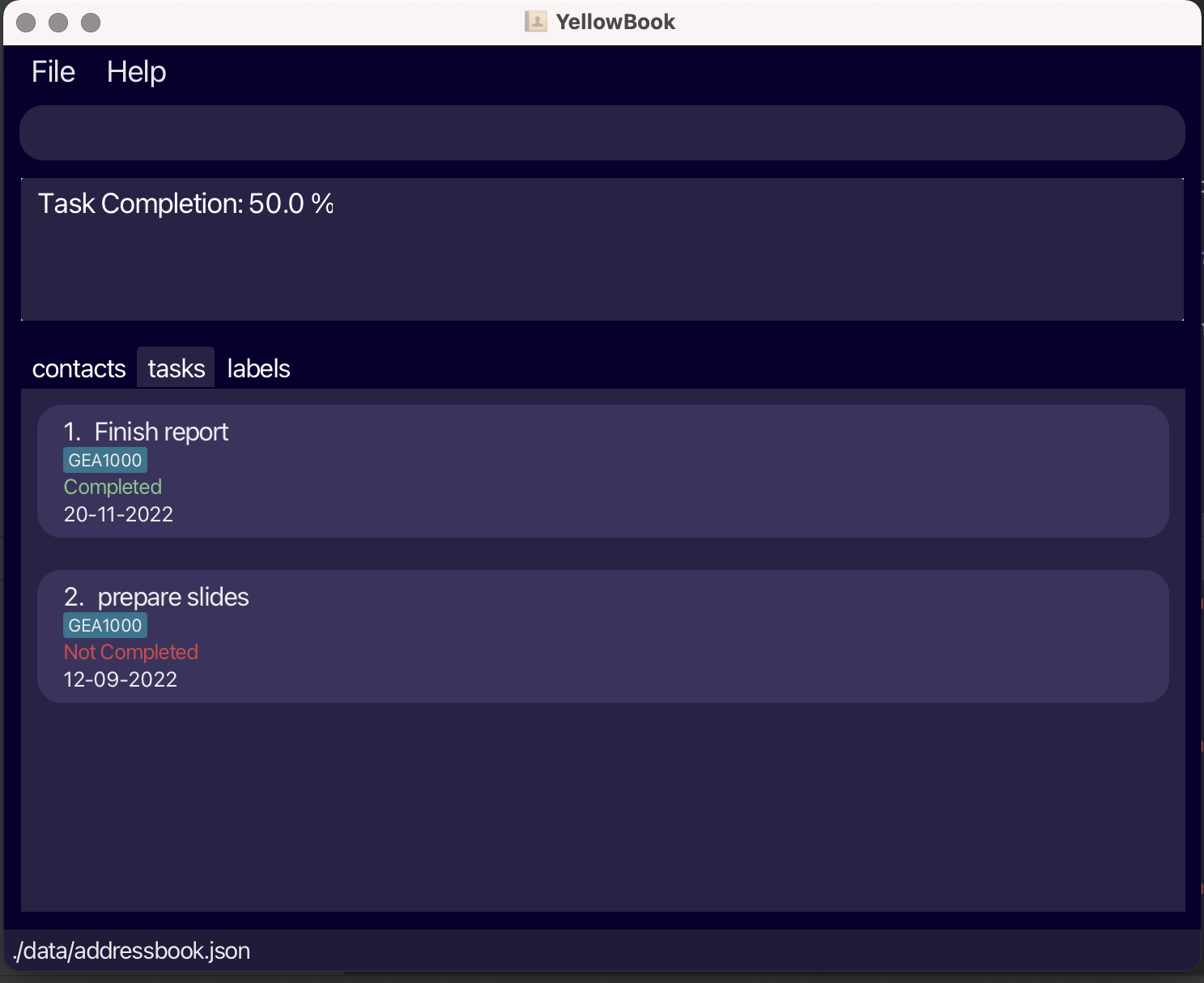
Showing the percentage of tasks with the specified tags that are completed: progressT
Shows the percentage of tasks whose label(s) contain any of the given keywords that are complete to one decimal place of accuracy.
Format: progressT KEYWORD [MORE_KEYWORDS]…
-
The filter is case-sensitive, e.g.
cs2103twill not matchCS2103T. -
Only full words will be matched. e.g.
cs2103twill not matchcs2103. -
Tasks with labels matching at least one keyword will be returned.
-
Both complete and incomplete tasks are listed.
-
Both archived and unarchived tasks are listed.
-
Tasks with deadlines that are already past are also listed.
![]() There will be an error if you:
There will be an error if you:
- Do not adhere to label name constraints. Label names must be alphanumeric with no spaces.
Example:
-
progressT cs2103twill show the percentage of tasks with labelcs2103tthat are completed, then list all tasks with labels matching at least one keyword.
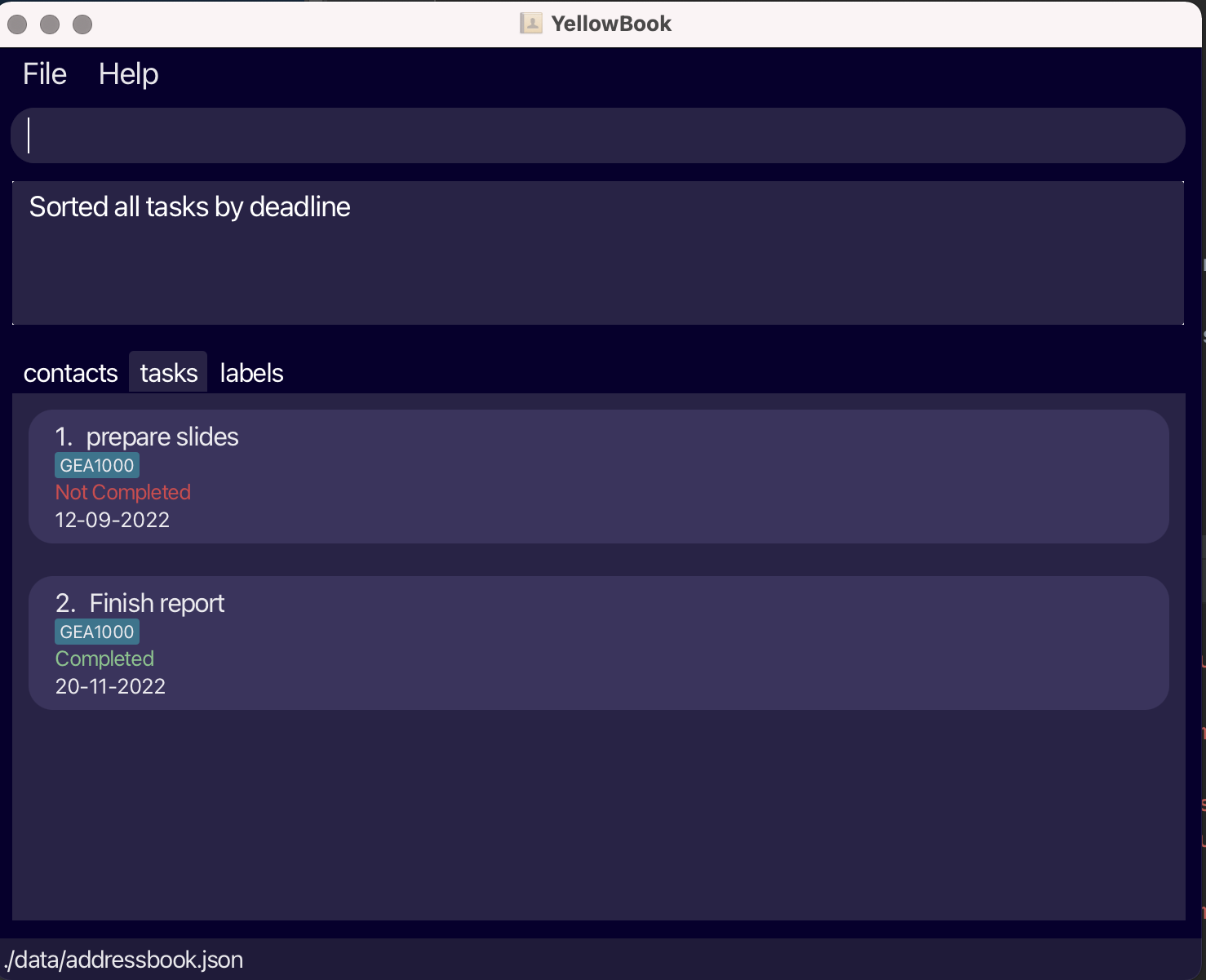
Sorting all tasks by deadline: sortD
Sorts all tasks in the task list by deadline.
Format: sortD
-
Adding or editing a task will not affect the sorted order of the task list.
-
The list remains in this sorted order until a different sort command is used.
Sorting all tasks by id: sortI
Sorts all tasks in the task list by id.
Format: sortI
-
Id is the order in which the tasks were added.
-
Adding or editing a task will not affect the sorted order of the task list.
-
The list remains in this sorted order until a different sort command is used.
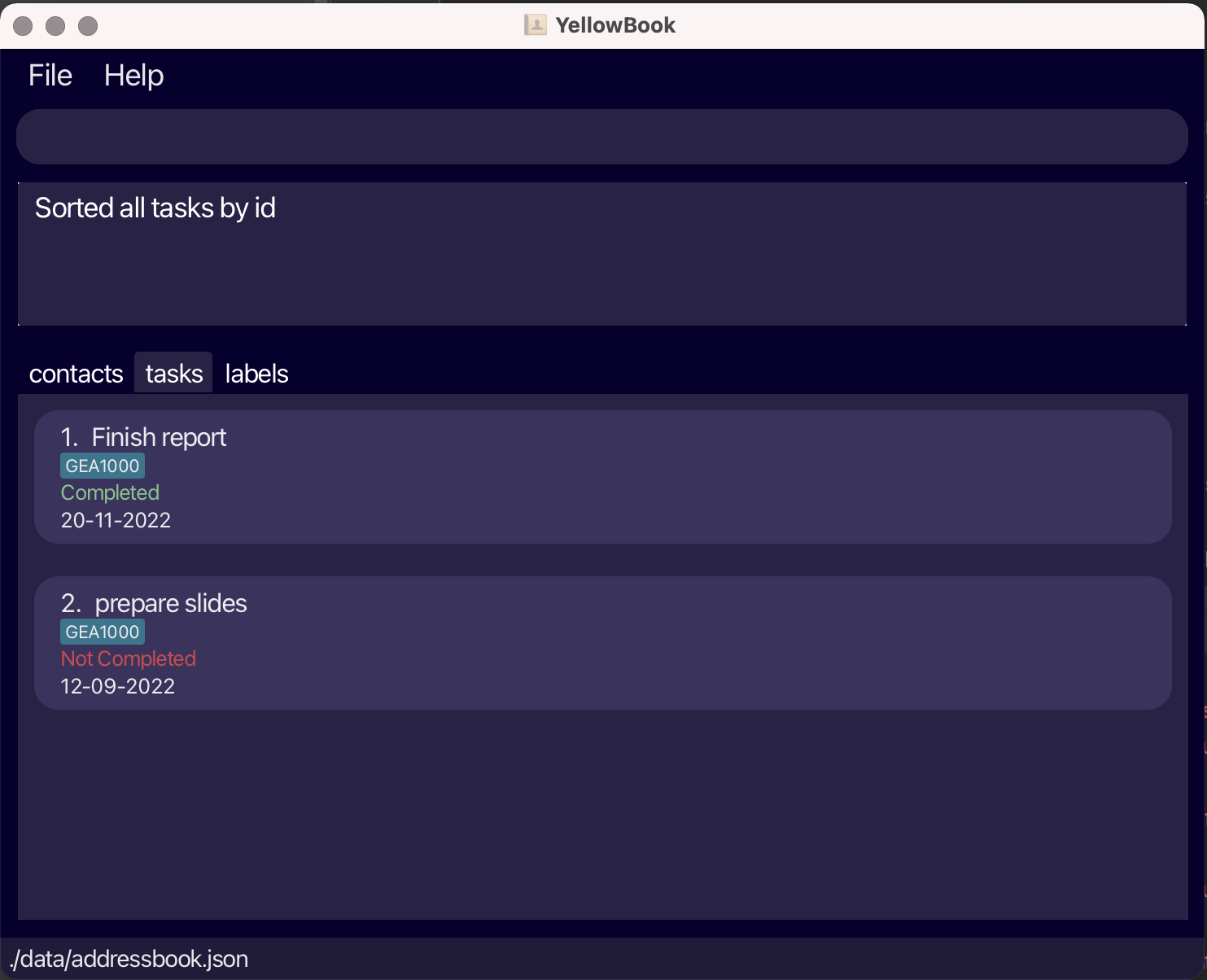
Section 3: Labels
These commands allow you to further organise people and tasks into subgroups depending on the nature of the project you are working on together. Whether it be a software engineering module or a business pitch, you can customise every person and task. With our label feature, managing your numerous projects on the go has just gotten a lot easier.
![]() Notes on labels:
Notes on labels:
-
Labels must be alphanumeric and one word long.
-
Labels used in commands are case-sensitive. e.g.
CS2103Tis different fromcs2103t.
Adding a label to a contact/task: addL
Adds a label to an existing contact/task in YellowBook. At the same time, the label is added to the label list, shown under the “tags” tab of the app. This list is unique, meaning each label with a distinct name is only shown once, even if more than one contact/task has the same label.
Format: addL c/INDEX t/INDEX l/label_NAME
-
Index of a contact is its index number on the currently shown contact list.
-
Index of a task is its index number on the currently shown task list.
![]() There will be an error if you:
There will be an error if you:
-
Do not adhere to the field constraints.
-
Specify more than one contact or more than one task.
-
Try to delete a label from a contact or task that does not have it.
-
Enter 0 or a negative number as INDEX.
-
Enter a number greater than the currently shown list size as INDEX.
Example:
-
addL c/3 t/12 l/CS2103Twill add the label “CS2103T” to the 3rd contact on the contact list and 12th task on the task list.
Listing all labels: listL
Shows all labels stored in the label list.
Format: listL
Deleting a label from a contact/task: deleteL
Deletes a label from an existing contact/task in YellowBook.
If contact/task is last remaining contact/task with said label, label is deleted from the label list. Otherwise, it is only deleted from the specified contact/task label list.
Format: deleteL c/INDEX t/INDEX l/label_NAME
-
Index of a contact is its index number on the currently shown contact list.
-
Index of a task is its index number on the currently shown task list.
![]() There will be an error if you:
There will be an error if you:
-
Do not adhere to the field constraints.
-
Specify more than one contact or more than one task.
-
Try to add a label to a contact or task that already has it.
-
Enter 0 or a negative number as INDEX.
-
Enter a number greater than the currently shown list size as INDEX.
Example:
-
deleteL c/12 t/14 l/CS2101will remove the label “CS2101” from the 12th contact on the contact list and 14th task on the task list.
Deleting all contacts and tasks by label: deleteA
Deletes all contacts and tasks that contain the label(s) specified. The label is also deleted.
Format: deleteA LABEL_NAME [MORE_LABEL_NAMES]...
- If a contact/task has multiple labels, it will not be deleted as long as it has at least one label. Instead, the labels will be removed from the contact/task.
![]() There will be an error if you:
There will be an error if you:
-
Do not adhere to the field constraints.
-
Try to delete a label that does not exist.
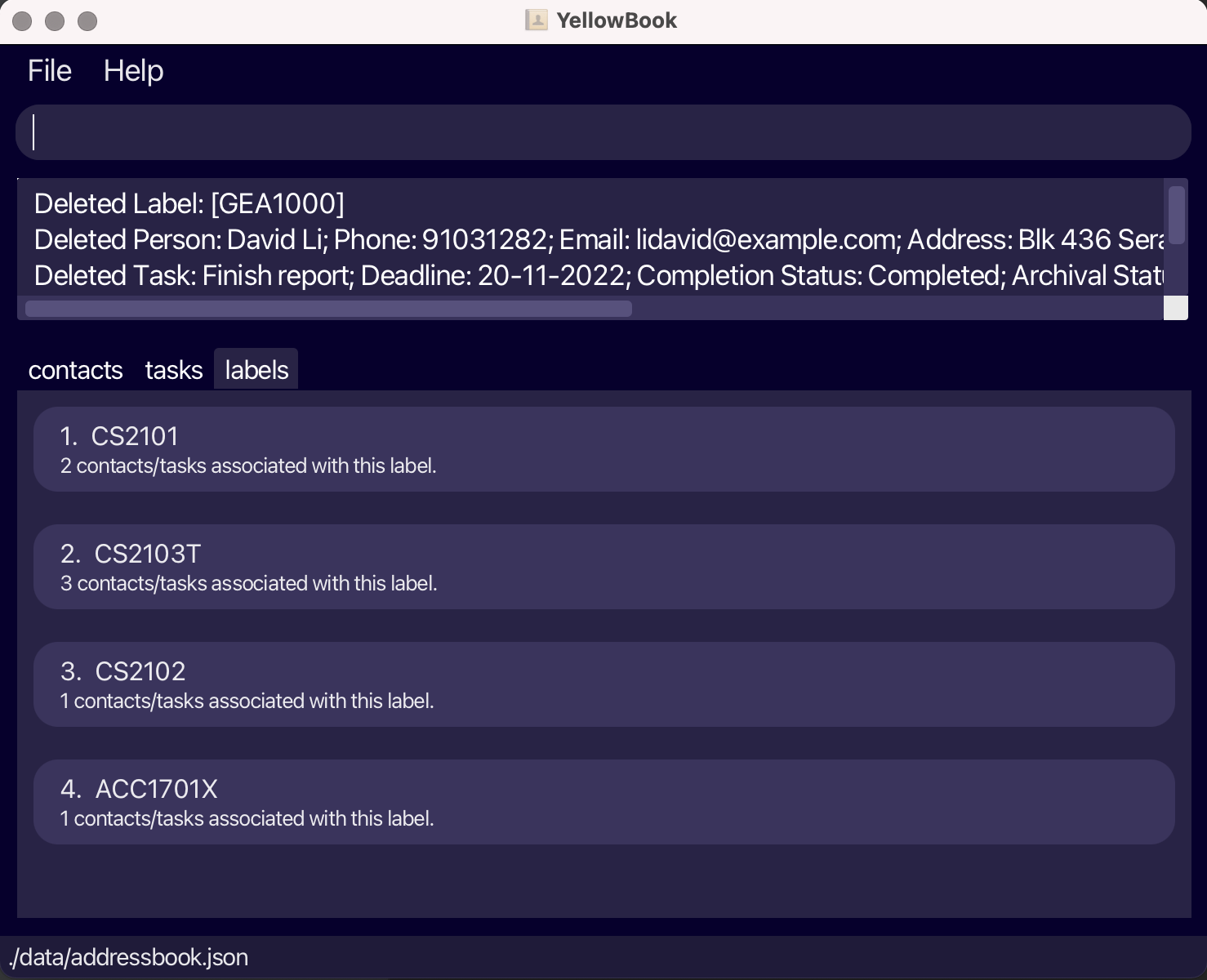
Section 4: Other Useful Features
Viewing help: help
Shows a window with a link to this user guide and latest release of YellowBook.
Format: help
Undoing a command: undo
Undoes the last command.
Format: undo
-
For exceptionally large contact/task lists, it may take a few seconds to undo the command.
-
Undo is not available for commands that do not modify the contact/task data (e.g. listC, listT, help, findC, findT, filterC, filterT etc.)
Redoing a command: redo
Redoes the last command.
Format: redo
-
For exceptionally large contact/task lists, it may take a few seconds to redo the command.
-
Redo is not available for commands that do not modify the contact/task data (e.g. listC, listT, help, findC, findT, filterC, filterT etc.)
Clearing YellowBook data: clear
Clears all data from YellowBook.
Format: clear
Exiting YellowBook: exit
Closes the YellowBook program.
Format: exit
Automatic tab switching
Depending on the command you enter, you will see the open tab in the GUI switch automatically. For example, when using a task-related command, the tab switches to “Task” and the task list is displayed.
The result of the entered command is displayed. For example, after adding a new contact, the list shown on the GUI is the updated list with your new contact included.
YellowBook data
Saving the data
YellowBook data are saved in the hard disk automatically after any command that changes the data. There is no need to save manually.
Editing the data file
YellowBook data are saved as a JSON file [JAR file location]/data/yellowbook.json. You are strongly encouraged to use the YellowBook application’s commands rather than edit the data file directly as there may be invalid data entered.
Advanced users who wish to edit the data file should note the following:
-
Idfield of aContactis unique and should comply with the string representation of Java UUID -
Idfield of aTaskis unique and should be an number greater than zero - Fields for
Contacts,TasksandLabelsshould comply with the respective field constraints.
![]() If your changes to the data file makes its format invalid, YellowBook will discard all data and start with an empty data file at the next run.
If your changes to the data file makes its format invalid, YellowBook will discard all data and start with an empty data file at the next run.
FAQ
Q: How do I transfer my data to another computer?
A: Install the app in the other computer and overwrite the empty data file it creates with the file that contains the data of your previous YellowBook home folder.
Q: My contact’s full name includes special characters (e.g. s/o). Why can’t I add it?
A: YellowBook does not currently support special characters in names as it is not a critical feature for students managing their project contacts. We will be adding support for special characters in future versions.
Command summary
| Command | Mnemonic | Format, Examples |
|---|---|---|
| help | - | help |
| undo | - | undo |
| redo | - | redo |
| clear | - | clear |
| exit | - | exit |
| listC | list Contact | listC |
| addC | add Contact |
addC n/NAME p/PHONE_NUMBER e/EMAIL a/ADDRESS [r/REMARK] e.g., addC n/John Doe p/98765432 e/johnd@example.com a/John street, block 123, #01-01
|
| deleteC | delete Contact |
deleteC INDEX e.g., deleteC 1
|
| editC | edit Contact |
editC INDEX [n/NAME] [p/PHONE] [e/EMAIL] [a/ADDRESS] [r/REMARK] e.g., editC 1 n/John p/12345678
|
| findC | find Contact |
findC [n/NAME] [p/PHONE] [e/EMAIL] [a/ADDRESS] [r/REMARK] e.g., findC n/Ferb
|
| filterC | filter Contact |
filterC KEYWORD [MORE_KEYWORDS] e.g., filterC cs2103t
|
| copyC | copy Contact emails |
copyC KEYWORD e.g. copyC CS2103T
|
| listT | list Tasks | listT |
| listAT | list Archived Tasks | listAT |
| addT | add Task |
addT d/DESCRIPTION D/DEADLINE e.g., addT d/buy milk D/12-09-2022
|
| deleteT | delete Tasks |
deleteT INDEX e.g., deleteT 12
|
| editT | edit Tasks |
editT INDEX [d/DESCRIPTION] [D/DEADLINE] e.g., editT 1 d/sleep D/22-10-2022
|
| markT | mark Task as completed |
markT INDEX e.g., markT 1
|
| unmarkT | unmark Task as not completed |
unmarkT INDEX e.g., unmarkT 1
|
| archiveT | archive Task |
archiveT INDEX e.g., archiveT 1
|
| unarchiveT | unarchive Task |
unarchiveT INDEX e.g., unarchiveT 1
|
| findT | find Tasks |
findT [d/DESCRIPTION] [D/DEADLINE] [s/STATUS] e.g., findT d/homework
|
| filterT | filter Tasks |
filterT KEYWORD [MORE_KEYWORDS] e.g., filterT cs2103t
|
| remindT | remind Tasks due on/before certain date |
remindT DEADLINE e.g., remindT 12-09-2022
|
| progressT | progress of Task with label |
progressT KEYWORD [MORE_KEYWORDS] e.g., progressT cs2103t
|
| sortD | sort by Deadline | sortD |
| sortI | sort by Id | sortI |
| listL | list Labels | listL |
| addL | add Label to contact or task |
addL c/INDEX l/LABEL_NAME [l/MORE_LABELS] OR addL t/INDEX l/LABEL_NAME [l/MORE_LABELS] OR addL c/INDEX t/INDEX l/LABEL_NAME [l/MORE_LABELS] e.g., addL c/3 t/12 l/CS2103T
|
| deleteL | delete Label from contact or task |
deleteL c/INDEX l/LABEL_NAME [l/MORE_LABELS] OR deleteL t/INDEX l/LABEL_NAME [l/MORE_LABELS] OR deleteL c/INDEX t/INDEX l/LABEL_NAME [l/MORE_LABELS] e.g., deleteL c/12 t/14 l/CS2101
|
| deleteA | delete All contact(s)/task(s) with tag |
deleteA LABEL_NAME [MORE_LABEL_NAMES] e.g., deleteA cs2103t
|